Remote desktop tools have become an indispensable part of modern work environments, enabling users to access and control computers remotely. Among the various options available, two of the most popular remote desktop protocols are Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) and Virtual Network Computing (VNC). Each has its unique strengths, weaknesses, and ideal use cases. This article aims to provide a comprehensive comparison of RDP and VNC, helping you choose the best remote desktop tool for your needs.
Table of Contents
What is RDP?

Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) is a proprietary protocol developed by Microsoft, allowing users to connect to another computer over a network connection. RDP is built into Windows operating systems and is also available for macOS, Linux, and other platforms through third-party applications. It provides a graphical interface to the user, making remote control of a computer as if you were sitting right in front of it.
How Does RDP Work?
RDP works by transmitting the screen image of the remote machine to the client machine and sending the client’s input (keyboard and mouse actions) back to the server. The protocol uses port 3389 by default and supports features such as:
- Session reconnection: Allows users to reconnect to their remote session.
- Clipboard sharing: Enables copying and pasting between local and remote machines.Resource redirection: Allows the use of local devices (printers, drives) on the remote session.Network level authentication: Enhances security by requiring the user to authenticate before establishing a session.
Key Features of RDP

What is VNC?
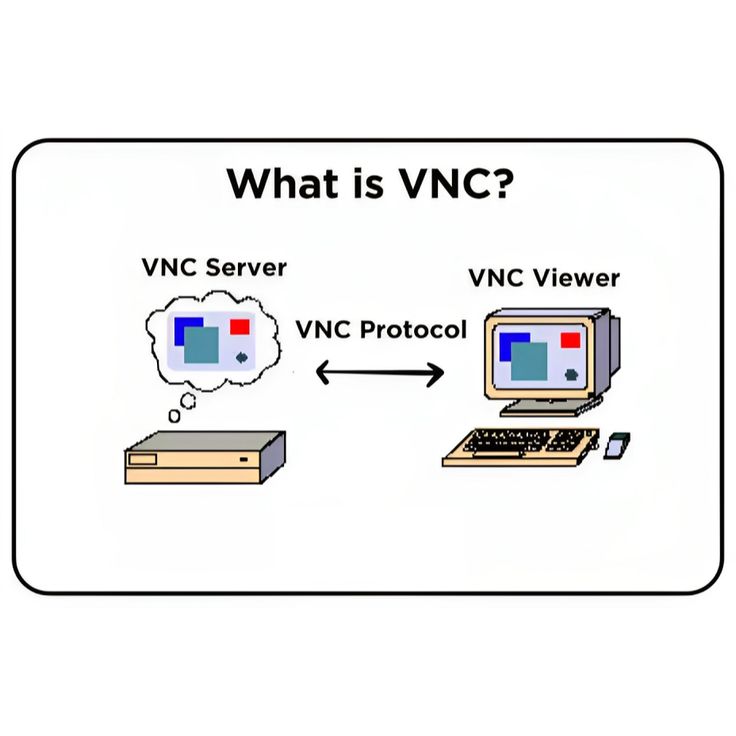
Virtual Network Computing is an open-source remote desktop protocol that provides cross-platform compatibility, allowing users to control any machine regardless of the operating system. It works on a client-server model and uses the Remote Framebuffer (RFB) protocol to transmit the screen and input events.
How Does VNC Work?
It transmits the framebuffer (screen) of the remote machine to the client and sends input events from the client back to the server. The protocol operates over TCP/IP and uses port 5900 by default. It is highly flexible and can be used in various environments, from home networks to large enterprise setups.
Key Features of VNC
Cross-Platform Compatibility: Works on multiple operating systems, including Windows, macOS, Linux, and UNIX.
Flexibility: Can be used for a wide range of applications, from personal use to enterprise-level deployments.
Open Source: Many Virtual Network Computing implementations are open source, allowing customization and flexibility.
Simplicity: Simple setup and configuration make it accessible to users of all skill levels.
File Transfer: Some Virtual Network Computing implementations support file transfer between local and remote machines.
Comparing RDP and VNC
Performance
RDP: Known for its high performance, especially on high-speed networks. RDP is optimized for multimedia content and offers a smooth experience even over limited bandwidth connections. Its ability to compress data and efficiently handle screen updates makes it suitable for various applications, including video streaming and gaming.
VNC: Performance can vary depending on the implementation and network conditions. Virtual Network Computing is not as optimized for multimedia content as RDP and may experience lag or slower response times, especially over low-bandwidth connections. However, It’s simplicity and flexibility make it suitable for many tasks, such as remote troubleshooting and administration.
Security
RDP: Offers robust security features, including encryption, network-level authentication, and support for Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) and Transport Layer Security (TLS). These features help protect against unauthorized access and data breaches, making RDP a suitable choice for enterprise environments.
VNC: Security features can vary depending on the implementation. Some versions offer encryption and password protection, while others may require additional configuration or third-party tools to enhance security. Users should carefully evaluate the security features of their chosen VNC implementation to ensure it meets their needs.
Ease of Use
RDP: Seamless integration with Windows operating systems makes RDP easy to set up and use for Windows users. The built-in RDP client simplifies the process, and the intuitive graphical interface provides a user-friendly experience.
VNC: Offers a straightforward setup and configuration process, making it accessible to users of all skill levels. Cross-platform compatibility ensures that Virtual Network Computing can be used in diverse environments, but the user experience may vary depending on the chosen Virtual Network Computing client and server software.
Cross-Platform Compatibility
RDP: Primarily designed for Windows environments, though clients are available for macOS, Linux, iOS, and Android. Integration with non-Windows systems may require additional configuration and third-party tools.
VNC: Truly cross-platform, with support for Windows, macOS, Linux, UNIX, and more. VNC’s flexibility and wide compatibility make it a versatile choice for mixed-OS environments.
Resource Redirection
RDP: Excels in resource redirection, allowing users to access local devices (printers, drives, USB devices) from the remote session. This feature enhances productivity by enabling seamless integration between local and remote resources.
VNC: Basic implementations may not support advanced resource redirection features. Some VNC versions offer file transfer capabilities, but the extent of resource redirection depends on the chosen implementation.
Scalability
RDP: Highly scalable, suitable for both small businesses and large enterprises. RDP supports multiple concurrent sessions on Windows Server, making it ideal for environments with numerous remote users.
VNC: Also scalable, but may require more effort to configure and manage in large deployments. Some VNC implementations support multiple sessions, but scalability features can vary.
Cost
RDP: Included with Windows operating systems, making it cost-effective for Windows users. Additional costs may arise from third-party RDP clients for non-Windows platforms or advanced features.
VNC: Many VNC implementations are open source and free to use, but commercial versions with additional features and support are also available. The cost will depend on the chosen VNC software and any additional tools or services required.
Use Cases for RDP and VNC
When to Use RDP
- Enterprise Environments: RDP’s security, performance, and scalability make it ideal for large organizations with strict security requirements and numerous remote users.
- Windows-Centric Setups: Seamless integration with Windows operating systems ensures a smooth user experience and easy setup for Windows users.
- Multimedia Applications: RDP’s optimized performance for high-speed networks and multimedia content makes it suitable for applications requiring smooth video and audio streaming.
When to Use VNC
- Cross-Platform Compatibility: It’s ability to work across multiple operating systems makes it an excellent choice for mixed-OS environments.
- Simple Remote Support: It’s straightforward setup and configuration make it ideal for remote troubleshooting and support, especially in small businesses or home networks.
- Customization and Flexibility: Open-source VNC implementations allow for customization to meet specific needs, making it suitable for a wide range of applications.
Choosing the Right Tool for Your Needs
When deciding between RDP and VNC, consider the following factors:
- Operating System: If your environment is predominantly Windows-based, RDP may offer the best integration and performance. For mixed-OS environments, VNC provides greater flexibility.
- Security Requirements: Evaluate the security features of each protocol to ensure they meet your organization’s standards. RDP offers robust security out-of-the-box, while VNC may require additional configuration.
- Performance Needs: For applications requiring high performance and multimedia content, RDP’s optimization can provide a smoother experience. VNC may be sufficient for less demanding tasks.
- Scalability: Consider the number of remote users and the scalability features of each protocol. RDP is well-suited for large deployments, while VNC can be scaled with additional configuration.
- Cost: Evaluate the cost of each solution, including any licensing fees for commercial software and additional tools or services required.
Conclusion
Both RDP and VNC are powerful remote desktop tools with unique strengths and weaknesses. RDP excels in performance, security, and seamless integration with Windows environments, making it ideal for enterprise use and Windows-centric setups. VNC offers cross-platform compatibility, simplicity, and flexibility, making it a versatile choice for mixed-OS environments and remote support.
Ultimately, the best remote desktop tool for your needs will depend on your specific requirements, including operating system compatibility, security needs, performance expectations, scalability, and cost considerations. By carefully evaluating these factors, you can choose the remote desktop tool that best fits your needs and ensures a seamless and productive remote computing experience.