Welcome to the backbone of digital data exchange — File Transfer Protocol. In the intricate web of interconnected systems, FTP stands as a stalwart, facilitating the seamless transfer of files between computers since the early days of the internet. Its simplicity and versatility make it a timeless protocol, adapting to the evolving landscape of technology.
In this introduction, we will delve deeper into its workings, explore its various applications, and discuss best practices for maximizing its potential. Whether you are a seasoned IT professional or a curious enthusiast, understanding FTP is a valuable asset in navigating the digital landscape and ensuring efficient data exchange across networks.
Table of Contents
What is FTP?
File Transfer Protocol serves as a foundational and essential protocol in the realm of computer networking, enabling the seamless exchange of files between computers over a network. Since its inception in the early days of the internet, FTP has played a pivotal role in facilitating the transfer of data, whether it be for uploading website content, sharing files between users, or managing remote servers.
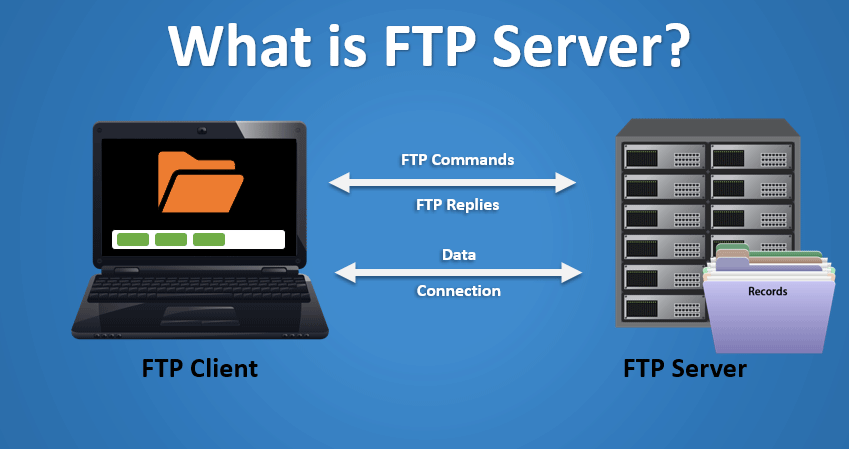
It operates on a client-server architecture, where one computer acts as the server hosting the files, and another serves as the client seeking to download or upload data. The protocol utilizes a set of rules to govern the reliable transmission of files, ensuring efficient and secure data exchange.
Is It Secure?
It does not provide inherent security measures, as data transmitted via FTP is sent in plain text, making it susceptible to eavesdropping and unauthorized access. However, to address these security concerns, two secure variations of FTP have been developed:
- FTPS : This extension of FTP adds a layer of security through the use of Transport Layer Security (TLS) or Secure Sockets Layer (SSL) protocols. By encrypting the data during transit, FTPS mitigates the risk of data interception and unauthorized access. It provides a more secure method of file transfer compared to traditional FTP.
- SSH File Transfer Protocol: Despite its name, SFTP is a distinct protocol from FTP. It operates over an encrypted SSH (Secure Shell) connection, providing secure file transfer and a range of additional security features. It is widely favored for its robust security measures and is commonly used in various applications.
When dealing with sensitive information or transmitting data over untrusted networks, it is advisable to opt for FTPS or SFTP over traditional it. The choice between FTPS and SFTP often depends on specific security requirements and the infrastructure in place. Always ensure that your chosen file transfer method aligns with your security needs and industry standards.
Features
File Transfer Protocol is a standard network protocol that comes with a range of features designed to facilitate the efficient and reliable transfer of files between computers. Here are some key features :
File Transfer
It allows the transfer of files between a client and a server. Users can upload (send) files from their local system to a remote server or download (retrieve) files from a server to their local system.
Directory Listing
It enables users to view the contents of directories on both the local and remote systems. This directory listing provides information about files and subdirectories, allowing users to navigate the file structure.
Directory Navigation
Users can change directories on both the local and remote systems using commands. This feature allows for efficient organization and retrieval of files from specific directories.
Authentication
For secure and private file transfers, it supports user authentication. Users are required to provide a valid username and password to access it.
Permissions and Access Control
Its typically implement access controls and permissions to restrict or allow users’ access to certain directories and files. This ensures security and data integrity.
Passive and Active Mode
It can operate in passive or active mode for data transfer. Passive mode is commonly used when the client is behind a firewall, as it allows the client to open the data connection to the server. Active mode requires the server to open a connection to the client, which may pose challenges in certain network configurations.
Security Extensions
To address security concerns, it has evolved with secure extensions. FTPS adds TLS/SSL encryption to FTP, while SSH File Transfer Protocol uses the secure SSH protocol for file transfers.
Understanding these features allows users to make the most for their file transfer needs, while also considering security considerations based on the nature of the data being transferred.
Conclusion
In conclusion, File Transfer Protocol has stood the test of time as a fundamental and versatile protocol for transferring files across computer networks. From its humble beginnings in the early days of the internet to its continued relevance in today’s interconnected world, FTP remains a go-to solution for users seeking to exchange data reliably and efficiently.
In the ever-expanding landscape of data exchange, remains an integral tool, offering a balance of simplicity, efficiency, and security. Whether you’re a system administrator, a web developer, or an everyday user, a solid understanding of FTP empowers you to navigate the digital realm with confidence, ensuring seamless and secure file transfers in an interconnected world.


