In the realm of digital security and web browsing, Google’s URL blocklist plays a crucial role in safeguarding users from potentially harmful websites. This comprehensive guide delves into what the Google URL blocklist is, how it functions, its importance, and the impact it has on webmasters and internet users alike.
Table of Contents
What Is the Google URL Blocklist?

The Google URL blocklist, also known as Google’s Safe Browsing service, is a security measure implemented by Google to protect users from websites that host malware, phishing scams, and other malicious content. When a URL is added to this blocklist, it means that Google has identified the site as unsafe for users. As a result, browsers like Chrome, Firefox, and Safari (which utilize Google’s Safe Browsing API) will warn users when they attempt to visit such sites, helping prevent potential harm.
How Does the Google URL Blocklist Work?
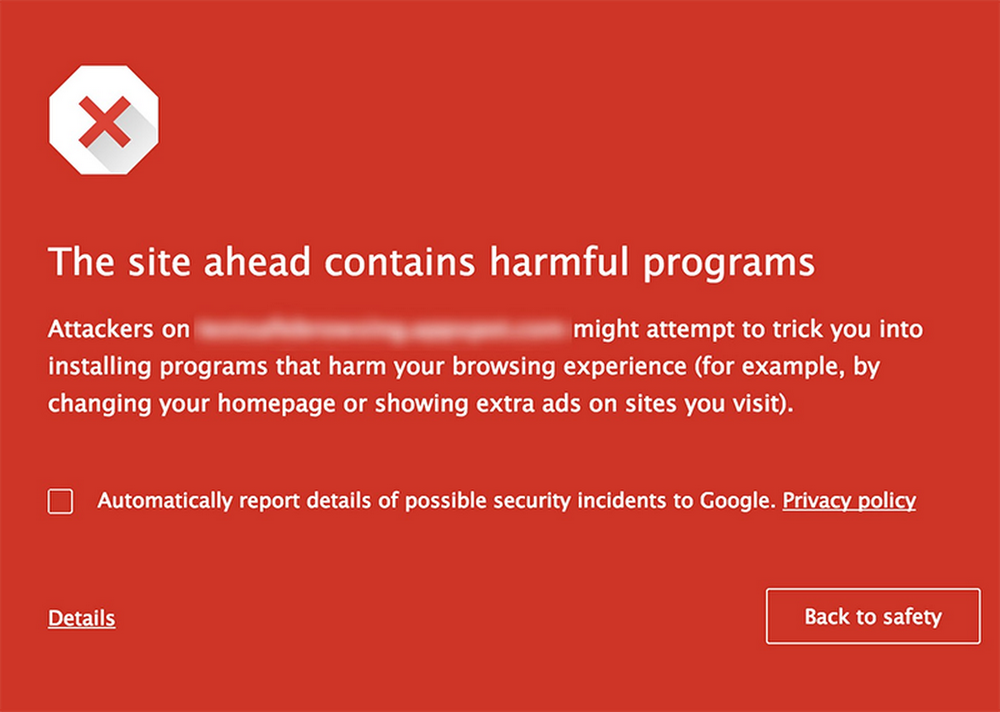
Google’s URL blocklist is part of the larger Safe Browsing initiative. This service continuously scans billions of URLs to identify unsafe websites. Here’s a step-by-step overview of how it works:
- Crawling and Analysis: Google’s web crawlers systematically scan the internet, analyzing websites for signs of malicious activity. This includes looking for malware, phishing content, and other threats.
- Threat Identification: When a potential threat is detected, Google’s systems evaluate the severity and nature of the threat. This involves automated systems and, in some cases, human review.
- Blocklist Update: Once a website is confirmed to be unsafe, its URL is added to the blocklist. Google then updates the Safe Browsing database, which is accessed by web browsers and other applications to check URLs in real time.
- User Alerts: When a user attempts to visit a blocked URL, their browser checks the URL against the Safe Browsing database. If the URL is found in the database, the browser displays a warning message, advising the user not to proceed.
Importance of the Google URL Blocklist
The primary goal of the Google URL blocklist is to enhance online security. Here are some key reasons why this service is vital:

- Protection Against Malware: Malware can cause significant damage to users’ devices, including data theft, system corruption, and unauthorized access. By blocking URLs that host malware, Google helps protect users from these threats.
- Phishing Prevention: Phishing sites trick users into revealing sensitive information such as passwords and credit card numbers. The URL blocklist helps prevent users from falling victim to these scams.
- Maintaining Browser Security: The integration of Google’s Safe Browsing service with major web browsers ensures a wide-reaching impact, protecting millions of users worldwide.
- Building User Trust: Knowing that Google actively works to identify and block harmful websites builds trust among internet users, encouraging them to browse the web more confidently.
Impact on Webmasters
For webmasters, having a URL added to Google’s blocklist can have significant implications:
- Traffic Loss: Being blocklisted can lead to a dramatic drop in website traffic as users are warned to avoid the site.
- Reputation Damage: A blocklisted site may suffer damage to its reputation, as users may associate it with malicious activity, even if the issues are resolved later.
- SEO Penalties: Blocklisted sites may experience negative impacts on their search engine rankings, as Google aims to prioritize safe and trustworthy websites in its search results.
Steps to Avoid Being Blocklisted
To prevent your website from being added to Google’s URL blocklist, consider the following best practices:

- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits to identify and fix vulnerabilities on your website.
- Use HTTPS: Secure your website with HTTPS to encrypt data transmitted between your site and its users.
- Update Software: Ensure that your website’s software, including CMS platforms, plugins, and themes, are always up-to-date to avoid security loopholes.
- Monitor for Malware: Use security tools to regularly scan your website for malware and other malicious content.
- Educate Yourself and Your Team: Stay informed about common web threats and educate your team on best practices for maintaining website security.
What to Do If Your Site Is Blocklisted
If your website is blocklisted by Google, follow these steps to resolve the issue:
- Identify the Problem: Use Google’s Search Console to check for security issues and understand why your site was blocklisted.
- Remove Malicious Content: Clean your website of any malware, phishing content, or other threats. This may involve restoring from a clean backup or using security tools to remove malicious code.
- Fix Vulnerabilities: Address the underlying vulnerabilities that allowed the malicious content to infiltrate your site in the first place. This could involve updating software, fixing code, or improving security practices.
- Request a Review: Once your site is clean and secure, request a review through Google’s Search Console. Google will re-evaluate your site and, if it is found to be safe, remove it from the blocklist.
The Future of Google’s URL Blocklist
As cyber threats continue to evolve, Google’s URL blocklist will likely become more sophisticated. Future enhancements may include improved detection algorithms, more frequent updates, and expanded integration with other security services. Additionally, Google may introduce more tools and resources to help webmasters proactively protect their sites from becoming targets of malicious activity.
Conclusion
The Google URL blocklist is a critical component of online security, protecting users from malicious websites and enhancing the overall safety of the internet. For webmasters, understanding how the blocklist works and taking proactive steps to secure their sites is essential to avoid the negative consequences of being blocklisted. As cyber threats continue to evolve, both users and website owners must remain vigilant and informed to navigate the digital landscape safely.
By prioritizing security and staying updated with best practices, we can all contribute to a safer and more trustworthy internet for everyone.



