Keeping the system date and time accurate on your server is crucial for ensuring smooth operation, especially for applications and services that depend on precise timing. The Plesk Admin Panel offers an intuitive way to manage date and time settings directly within its interface, allowing you to keep everything in sync. This article will guide you through the steps needed to update the system date and time in Plesk, including why it matters and tips for managing time zones effectively.
Table of Contents
Why System Date and Time Matter
Maintaining accurate date and time settings on your server is essential for several reasons:
- Scheduling: Applications, services, and scripts on your server often rely on the server time for scheduling tasks. If the system time is incorrect, scheduled tasks may run at the wrong time or fail entirely.
- Logging and Auditing: Accurate time settings ensure that log files and audit trails show the correct timestamps, making it easier to troubleshoot issues, track activity, and manage server security.
- Authentication and Security: Many security protocols rely on accurate system time to function correctly. An incorrect date and time can disrupt SSL certificate validation, token-based authentication, and other security mechanisms.
- Time-Sensitive Applications: Applications like databases, email servers, and scheduling systems require precise time management. Incorrect times can cause these applications to malfunction or experience errors.
With Plesk’s user-friendly interface, adjusting the system time on your server is straightforward. Here’s a step-by-step guide to ensure your system date and time are properly configured.
Step 1: Log in to Plesk Admin Panel
- Start by logging into the Plesk Admin Panel. You will need administrative access to make changes to server settings.
- Once logged in, navigate to the Tools & Settings section in the left-hand sidebar.
Step 2: Access the Date and Time Settings
- In the Tools & Settings menu, scroll down to locate Server Time under the General Settings section.
- Click on Server Time to open the date and time configuration page.

Step 3: Update the System Date and Time
Now that you’re in the date and time settings, you have a few options:
- Manually Adjust the Date and Time: You’ll see fields where you can enter the current date and time. Make sure to use the correct format for your region. Update the date and time by typing directly into these fields.
- Select the Time Zone: Ensure your server is set to the correct time zone. Select your preferred time zone from the drop-down menu if needed.
- Enable NTP Synchronization: If you want your server to automatically sync with an external time server, look for the Network Time Protocol (NTP) option. Enabling NTP ensures your server time stays accurate by syncing periodically with a reliable source.
Step 4: Save Your Changes
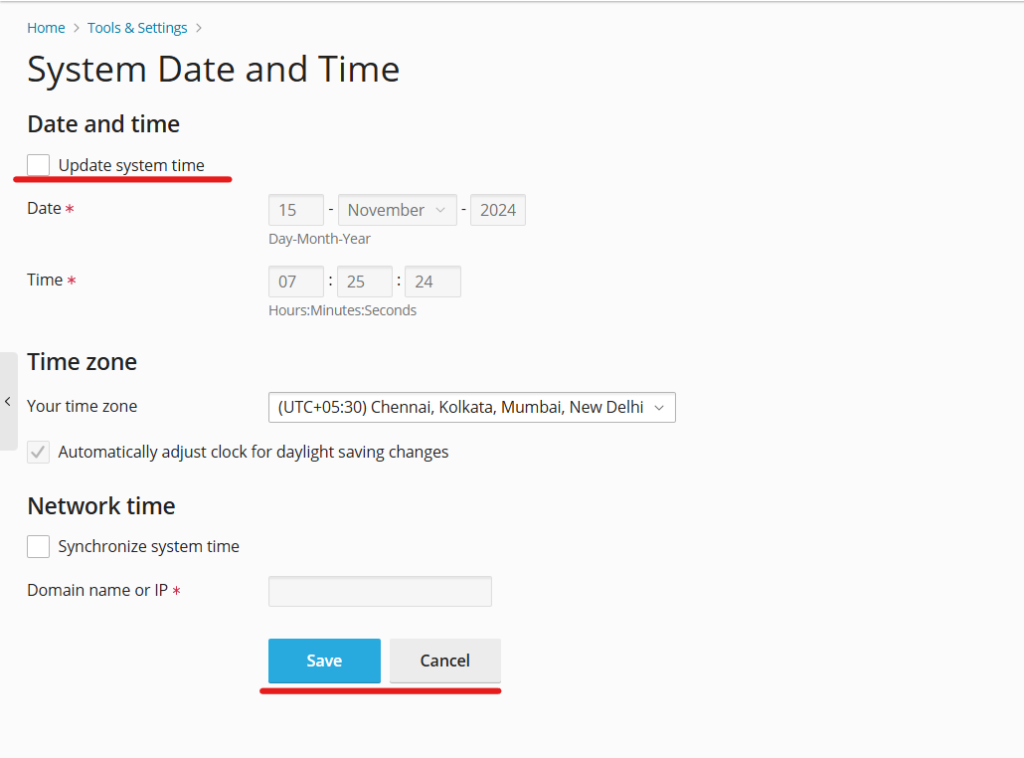
After adjusting the date, time, and time zone settings:
- Click Apply or OK to save your changes.
- Plesk will apply the new date and time settings, and your server’s clock will now reflect these adjustments.
Managing Time Zones in Plesk
Understanding time zones is essential, especially if your server is hosted in one region but serves users in multiple time zones. Here are some tips for setting the time zone effectively in Plesk:
- Use UTC for Global Servers: If your server serves users across various time zones, it’s often best to set the time zone to UTC (Coordinated Universal Time). UTC is a global time standard that avoids confusion due to daylight savings and local time shifts.
- Consider User Location: If your server’s users are primarily in one region, set the time zone to match their location. This will help ensure logs and application timestamps are easy to interpret for local users.
- Account for Daylight Savings: Some regions observe daylight saving time (DST), shifting the time forward or backward by one hour during certain parts of the year. If your server is in a region that observes DST, ensure it’s configured to handle these changes automatically.
Common Issues with Incorrect System Time and How to Fix Them
Sometimes, you may encounter issues if the server time isn’t set correctly. Here are some common issues and their solutions:
- Failed SSL/TLS Connections: If the server time is incorrect, SSL/TLS certificates may be seen as expired or invalid. Fix this by updating the system time to match the correct date.
- Incorrect Logs: If logs show the wrong timestamps, troubleshooting can become more difficult. Updating the date and time will solve this issue and make logs accurate.
- Authentication Failures: Protocols like Kerberos and OAuth require accurate time settings to work correctly. If you’re experiencing authentication issues, ensure the server time is accurate.
Importance of Using NTP Synchronization
The Network Time Protocol (NTP) allows your server to sync with an external time source, keeping the server time accurate without manual updates. Using NTP has several benefits:
- Consistency: NTP ensures that your server’s time remains consistent, even if there are minor drifts over time.
- Security: By syncing with trusted time servers, NTP can prevent certain security issues related to time discrepancies.
- Ease of Management: Once NTP is set up, it automatically maintains accurate server time, so you don’t have to manually adjust it.
To enable NTP in Plesk, navigate to Date & Time Settings, and look for an option to enable NTP or specify an NTP server. This ensures your server time stays accurate without regular manual adjustments.
Conclusion
Updating the system date and time in Plesk is a straightforward process that ensures smooth operation for your applications, scheduling, logging, and security protocols. By following these steps, you can easily set the correct date and time for your server, select the appropriate time zone, and enable NTP synchronization for accuracy. Accurate time settings on your server not only improve functionality but also enhance security and provide a better user experience. If you have any doubts/clarifications, you can contact your service provider.



