Email routing is a crucial aspect of managing email services for domains hosted in cPanel. It allows users to control how and where their email messages are delivered. In this guide, we will explore the various email routing options in cPanel, how to configure them, and the importance of selecting the appropriate settings for your email infrastructure.
Table of Contents
What is Email Routing?
Email routing refers to the process of determining the path that emails follow when they are sent to an email account on your domain. The routing settings dictate whether the email is handled by the local server, forwarded to an external mail server, or sent to a backup email server. Proper configuration of email routing ensures that your email reaches the intended recipients without delays or delivery issues.
Why is Email Routing Important?
- Efficient Email Delivery: Email routing ensures that emails are delivered efficiently, especially in cases where multiple mail servers or external mail services like Google Workspace or Microsoft 365 are in use.
- Prevents Mail Loops: Incorrect email routing configurations can lead to mail loops, where emails bounce between servers without reaching their destination.
- Backup Mail Services: Routing also helps maintain continuity by routing emails to backup mail servers in case the primary server is down.
- Optimized Server Usage: By configuring the correct routing settings, you can reduce unnecessary load on your local server, especially when using third-party email services.
Understanding Email Routing Options in cPanel
In cPanel, there are four main email routing options available:
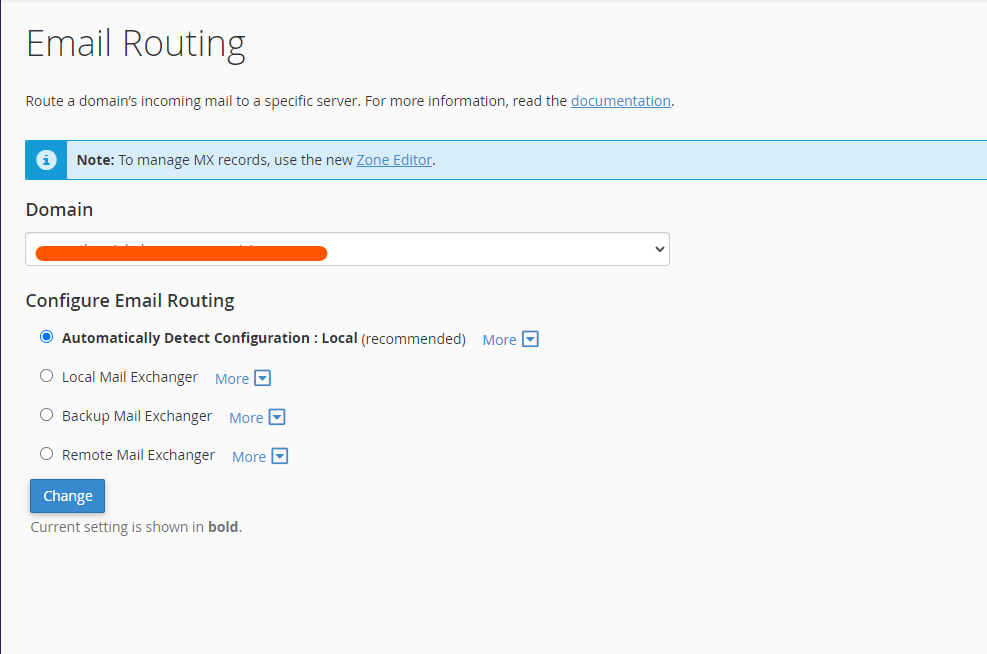
1. Local Mail Exchanger
This option is selected when you want the server hosting the domain to handle the email. When set to “Local Mail Exchanger,” cPanel will route all emails for your domain to the local server.
When to Use:
- When your email service is hosted on the same server as your website.
- If you do not use external email services like Google Workspace or Microsoft 365.
2. Backup Mail Exchanger
In this configuration, the server acts as a backup email server. If the primary email server is down, the emails are routed to the backup mail exchanger to store them until the primary server is back online.
When to Use:
- When you have a primary email server outside the cPanel environment.
- When you need redundancy in your email system to prevent email loss during server downtime.
3. Remote Mail Exchanger
This option should be selected if you are using an external email service to handle your domain’s emails. The local server will not attempt to handle the email delivery, and instead, all incoming emails will be routed to the external server.
When to Use:
- If you use third-party email services like Google Workspace or Microsoft 365.
- If you want to offload email management to a dedicated email server.
4. Automatic Detection
This option allows cPanel to automatically detect the best routing option based on your MX (Mail Exchanger) records. The server evaluates your domain’s DNS MX records to determine whether to route email to a local or remote server.
When to Use:
- When you are unsure of the best routing option to select.
- If you frequently update your MX records and want cPanel to adjust the routing dynamically.
How to Configure Email Routing in cPanel
Follow these steps to configure email routing in cPanel:
Log in to cPanel: Navigate to your cPanel dashboard by entering your domain URL followed by /cpanel.

Find the Email Routing Section: Scroll down to the “Email” section and click on the “Email Routing” option.
Select the Domain: If you have multiple domains, select the appropriate domain for which you want to configure email routing.
Choose the Routing Option: You will see the four routing options (Local, Backup, Remote, Automatic). Choose the appropriate option based on your email setup.
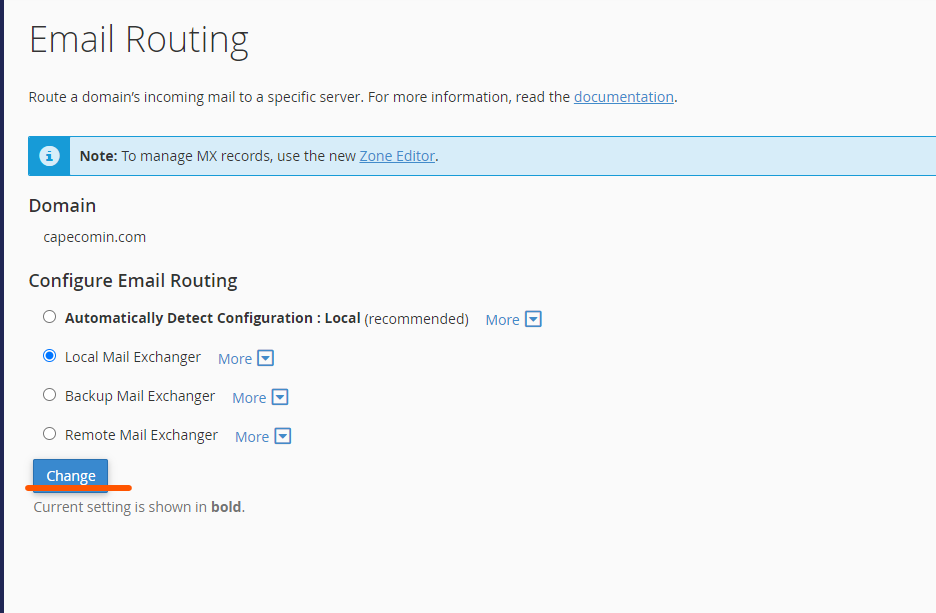
Save Changes: After selecting the desired routing option, click “Change” to save the configuration.
Understanding MX Records and Their Role in Email Routing
MX (Mail Exchanger) records are a type of DNS record that directs email traffic to a specific mail server. These records tell the domain where to send the email, and they work hand-in-hand with the email routing settings in cPanel.
Key Points to Remember:
- Priority in MX Records: MX records have priority levels (lower numbers mean higher priority). When configuring multiple MX records, emails will be routed to the server with the lowest priority value first. Backup mail servers typically have higher priority numbers.
- Changing MX Records: If you’re using external email services like Google Workspace, you’ll need to update your MX records to point to their mail servers.
- TTL (Time to Live): This value determines how long the DNS information for MX records is cached. Lower TTL values allow for quicker changes in routing but might increase DNS query traffic.
Common Scenarios for Email Routing Configuration
- Using Local Email Services If you are hosting both your website and email on the same server, the “Local Mail Exchanger” option is appropriate. No changes to your MX records are needed, and emails will be handled by your server.
- Using External Email Providers For businesses that use services like Google Workspace, you should set the routing to “Remote Mail Exchanger.” Update the MX records in your DNS zone to reflect the external provider’s mail servers.
- Backup Mail Setup If you have a secondary email server for redundancy, configure the backup server’s MX records with a higher priority number and set the routing to “Backup Mail Exchanger” to ensure emails are stored during outages.
Troubleshooting Common Email Routing Issues
1. Emails Not Being Delivered to the Right Mail Server
- Solution: Check your MX records and ensure they are pointing to the correct mail server. Also, verify that the correct email routing option is selected in cPanel.
2. Emails Are Bouncing Back
- Solution: This could be due to incorrect MX record priority or an outdated routing setting. Double-check your DNS configuration and routing selection.
3. Mail Loop Detected
- Solution: This occurs when emails are bouncing between servers without being delivered. Ensure that only one mail server is set to “Local Mail Exchanger” and verify your MX records.
Final Thoughts
Understanding and configuring email routing in cPanel is vital for ensuring smooth and efficient email delivery. Whether you are using local servers, external providers, or backup servers, selecting the correct email routing option is crucial. With a well-configured email system, you can avoid delivery delays, mail loops, and other email-related issues.
By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can confidently set up and manage your email routing settings in cPanel for optimal performance and reliability.



