In the vast and ever-expanding digital landscape, a domain names are more than just a web address—it’s the cornerstone of your online identity. Whether you’re launching a personal blog, an e-commerce site, or a corporate website, the domain name you choose plays a pivotal role in shaping how your audience perceives you and how easily they can find you online. This guide delves into the world of domain names, exploring what they are, why they’re important, and how to select the perfect one for your needs.
Table of Contents
What is a Domain Names?
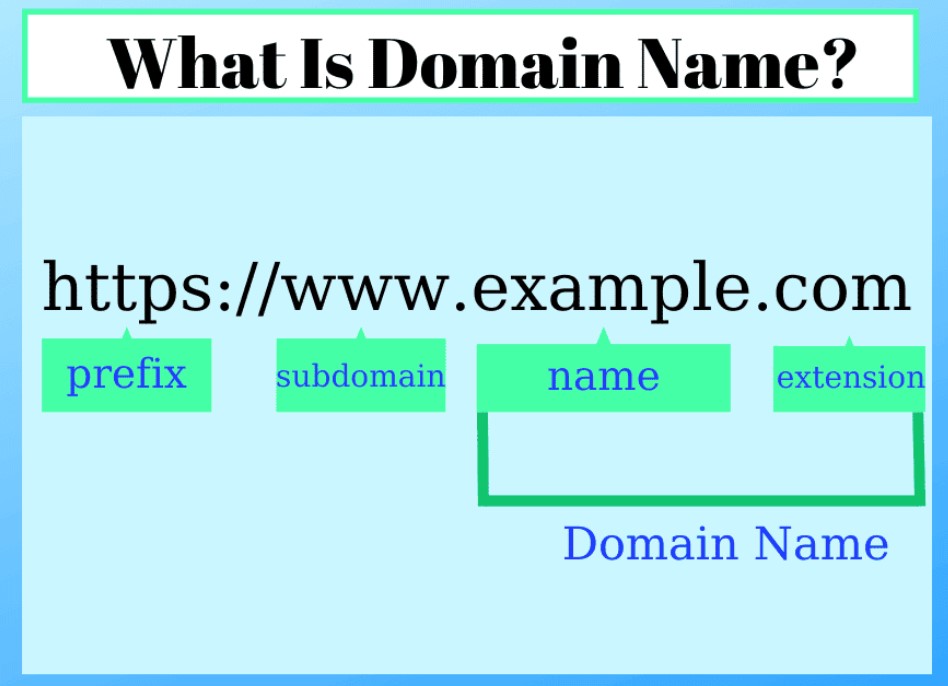
A domain name is essentially the address of your website on the internet. It’s what users type into their browser’s address bar to visit your site. For example, in the URL “https://www.google.com,” “example.com” is the domain name.
Every domain name corresponds to a numerical IP address that computers use to identify each other on the network. However, because IP addresses are difficult for humans to remember, domain names were created as a more user-friendly way of navigating the web. The Domain Name System (DNS) is what translates domain names into IP addresses, allowing users to access websites by entering easy-to-remember names instead of complex strings of numbers.
The Structure of a Domain Name
Domain names are structured in a hierarchical manner, consisting of several components:
- Top-Level Domain (TLD): This is the extension at the end of the domain name, such as .com, .org, .net, etc.
- Second-Level Domain (SLD): This is the part of the domain name that comes before the TLD. For example, in “example.com,” “example” is the SLD.
- Subdomain: This is an optional part that comes before the SLD. For instance, in “blog.example.com,” “blog” is the subdomain.
Together, these components form a complete domain name that can be used to access a website.
The History and Evolution of Domain Names
The concept of domain names was introduced in the early 1980s as the internet began to grow. The first domain name ever registered was “symbolics.com” on March 15, 1985. As the internet became more popular, the need for a structured and organized system to manage domain names became evident, leading to the development of the Domain Name System (DNS) in 1984.
The DNS allowed for a more scalable and decentralized approach to managing domain names, making it easier for new websites to be registered and accessed. Over time, the domain name industry has evolved significantly, with the introduction of new TLDs, the rise of domain name marketplaces, and the increasing importance of domain names in digital marketing and branding.
Why Domain Names Are Crucial for Your Business
A domain name is more than just a technical necessity—it’s a critical component of your brand’s identity and online presence. Here’s why having a strong domain name is essential for your business:
Branding
Your domain name is often the first thing potential customers see when they encounter your brand online. A memorable and relevant domain name can help reinforce your brand’s identity and make a lasting impression. Conversely, a confusing or hard-to-remember domain name can detract from your brand’s credibility and make it harder for customers to find you.
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
While exact-match domain names (EMDs) are no longer a guaranteed ticket to high search rankings, your domain name can still impact your SEO efforts. A domain name that includes relevant keywords can signal to search engines what your website is about, potentially boosting your site’s visibility in search results.
Trust and Credibility
A professional and well-chosen domain name can enhance your website’s trustworthiness. Customers are more likely to engage with and purchase from a website that has a credible domain name. On the other hand, a domain name that appears spammy or irrelevant can raise red flags and deter potential customers.
Memorability
A short, catchy, and relevant domain name is easier for users to remember, increasing the chances of repeat visits. A complex or unrelated domain name can lead to confusion and lost traffic.
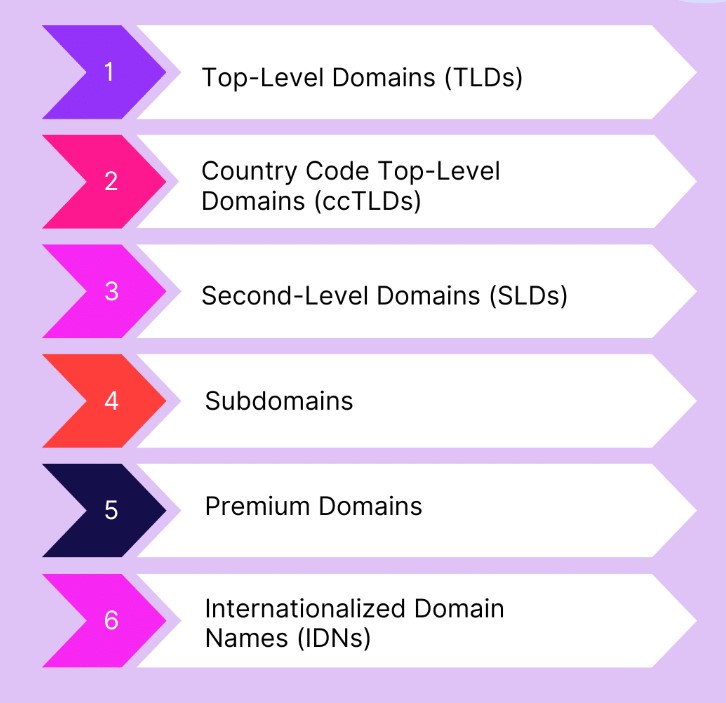
Different Types of Domain Names

Domain names come in various forms, each serving different purposes and catering to different audiences. Understanding the different types can help you choose the one that best suits your needs.
Top-Level Domains (TLDs)
TLDs are the highest level in the DNS hierarchy. The most common TLDs include:
- .com: Originally intended for commercial businesses, .com is now the most popular and widely recognized TLD.
- .org: Typically used by non-profit organizations.
- .net: Originally intended for network-related entities but is now used by various types of organizations.
- .edu: Restricted to accredited educational institutions.
- .gov: Reserved for government entities.
Country Code TLDs (ccTLDs)
ccTLDs are two-letter extensions that represent specific countries or territories. Examples include:
- .uk (United Kingdom)
- .ca (Canada)
- .au (Australia) Using a ccTLD can help you target a specific geographic market and signal to users that your business operates in a particular region.
Generic TLDs (gTLDs)
gTLDs are new domain extensions that go beyond the traditional TLDs. Examples include:
- .tech: Suitable for technology companies.
- .shop: Ideal for e-commerce businesses.
- .blog: Perfect for bloggers and content creators. These new gTLDs offer more flexibility and creativity in domain name selection, allowing businesses to choose extensions that align closely with their industry or niche.
How to Choose the Perfect Domain Name

Selecting the right domain name is a crucial step in establishing your online presence. Here are some tips to help you choose a domain name that resonates with your brand and audience:
Keep It Simple and Memorable
Your domain name should be easy to spell, pronounce, and remember. Avoid using complex words, hyphens, or numbers, as these can confuse users and make your domain name harder to recall.
Reflect Your Brand
Your domain name should align with your brand identity. It should convey the essence of your business and what you offer. Consider using your brand name as the domain name, or include keywords that describe your products or services.
Choose the Right Extension
While .com remains the most popular choice, don’t overlook other TLDs that might be more relevant to your industry or target audience. For example, if you’re running a non-profit, .org might be a better fit.
Check for Trademarks
Before registering a domain name, make sure it doesn’t infringe on any existing trademarks. This can help you avoid legal issues and ensure that your brand is unique.
Use Domain Name Generators
If you’re struggling to come up with a domain name, consider using online domain name generators. These tools can help you brainstorm ideas and find available domain names that match your criteria.
The Process of Registering a Domain Name
Once you’ve chosen the perfect domain name, the next step is to register it. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
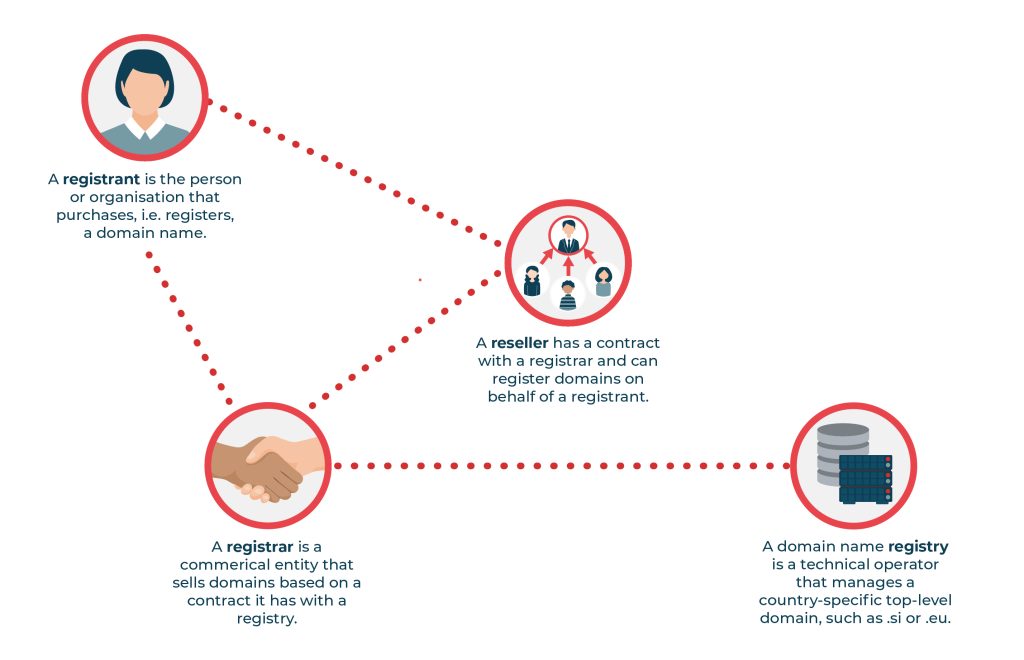
Step 1: Choose a Domain Registrar
A domain registrar is a company that manages the reservation of domain names. Popular registrars include GoDaddy, Namecheap, and Google Domains. Choose a reputable registrar that offers competitive pricing, good customer support, and additional services like domain privacy protection.
Step 2: Check Domain Availability
Use the registrar’s search tool to check if your desired domain name is available. If it’s already taken, the registrar will often suggest alternative names or extensions.
Step 3: Register the Domain
If your domain name is available, you can proceed with the registration. You’ll need to provide your contact information and choose the registration period (typically one year, with the option to renew).
Step 4: Set Up Domain Privacy Protection
Domain privacy protection is an optional service that hides your personal information from the public WHOIS database. This can help protect your privacy and reduce spam.
Step 5: Configure DNS Settings
Once your domain is registered, you’ll need to set up DNS records to point your domain to your website’s hosting server. This is a crucial step in making your website accessible online.
Step 6: Renew Your Domain
Domain names are typically registered on an annual basis, so it’s important to renew your domain before it expires. Many registrars offer auto-renewal options to ensure you don’t lose your domain.
Managing and Protecting Your Domain Name
After registering your domain name, it’s essential to manage and protect it effectively to ensure your online presence remains secure.

Setting Up DNS Records
DNS records are configurations that direct traffic to your website. Common DNS records include:
- A Record: Points your domain to an IP address.
- CNAME Record: Alias for your domain, pointing to another domain.
- MX Record: Directs email to your mail server. Properly configuring your DNS records is crucial for ensuring your website and email services function correctly.
Securing Your Domain Name
Domain security is vital for protecting your website from cyber threats. Here are some strategies to secure your domain name:
- Enable Two-Factor Authentication (2FA): Adding an extra layer of security to your registrar account can prevent unauthorized access.
- Lock Your Domain: Domain locking prevents unauthorized transfers of your domain to another registrar.
- Monitor WHOIS Data: Regularly check your WHOIS data to ensure it hasn’t been altered without your consent.
Preventing Domain Hijacking
Domain hijacking occurs when someone illegally gains control of your domain name. To prevent this, keep your registrar account secure, use strong passwords, and enable 2FA. Additionally, be cautious of phishing scams that attempt to steal your login credentials.
The Role of SSL Certificates
An SSL certificate encrypts the data transmitted between your website and its visitors, ensuring that sensitive information remains secure. It also signals to users that your website is trustworthy, as indicated by the “https://” in your web address. Many domain registrars offer SSL certificates as an add-on service.
The Future of Domain Names
The domain name industry is constantly evolving, with new trends and technologies shaping the way we think about and use domain names.
Trends in Domain Names
- New gTLDs: The introduction of new gTLDs has expanded the possibilities for domain name selection, allowing for more creative and industry-specific domains.
- Internationalized Domain Names (IDNs): IDNs allow domain names to be registered in non-Latin scripts, making the internet more accessible to users worldwide.
- Voice Search and Domains: As voice search becomes more popular, the demand for short and easy-to-pronounce domain names is likely to increase.
The Impact of Emerging Technologies
Emerging technologies like blockchain are also influencing the domain name industry. Blockchain domains, for example, offer decentralized alternatives to traditional domain names, providing users with more control over their online identity.
Predictions for the Domain Name Industry
As the internet continues to grow, the demand for domain names will likely increase. Businesses and individuals will continue to seek unique and memorable domain names that help them stand out in a crowded online space. Additionally, the importance of domain security will become even more critical as cyber threats evolve.
Conclusion
A domain name is a powerful tool that can significantly impact your online presence, brand identity, and business success. By understanding the importance of domain names, how they work, and how to choose and manage the right one, you can ensure that your website stands out and remains secure in the digital landscape. As the internet continues to evolve, so too will the role of domain names, making it more important than ever to stay informed and proactive in your domain management efforts.
4o


