URL masking, also known as URL cloaking or link masking, is a technique used to hide the actual URL of a webpage from the user and display a different URL in the browser’s address bar. This can be done for various reasons, including branding, affiliate marketing, or to create cleaner and more user-friendly URLs.
Table of Contents
What is URL Masking?
URL masking involves concealing the genuine domain name of a website, replacing it with an alternative name in the URL field of a user’s web browser.

It aims to conceal the initial URL, ensuring a smooth user experience by preserving the visual continuity of the original domain during the entire browsing session. This tutorial covers the basics of URL masking, its diverse applications, and effective implementation strategies for safeguarding sensitive data, boosting brand identity, and enhancing overall user satisfaction.
Types of URL masking
There are different types of URL masking techniques, each serving specific purposes. Here are some common types:
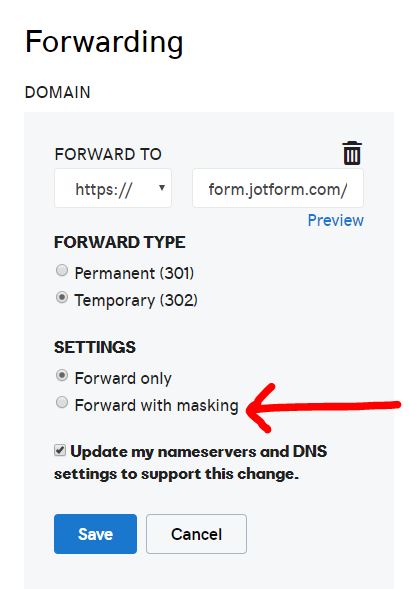
Domain masking
Domain masking is a technique where the original URL of a website is hidden, and a different domain name is displayed in the browser’s address bar. This is often done to provide a branded or customized appearance for a website while still utilizing the content and resources from another domain.
Frame masking
Frame masking is a method of URL masking where the content of one website is displayed within an HTML frame on another website. This technique involves embedding the content of the target website into a frame on the source website, allowing users to view the content seamlessly while the URL in the browser’s address bar reflects the source website’s domain.
Server-Side Scripting
The implementation of URL masking is achievable through server-side scripting languages like PHP, ASP, or JavaScript. In this process, the server-side script responds to a requested URL, retrieves content from an alternative URL, and subsequently presents this fetched content on the initial URL, preserving the original URL in the browser’s address bar.
URL Rewriting
URL rewriting is a method that alters the structure of a URL through server configurations or .htaccess files. This technique enables the server to internally associate a user-friendly URL with an actual URL, all without revealing the original URL in the address bar. Consequently, content from a different URL can be displayed while maintaining the appearance of the original URL.

Proxy Masking
Proxy masking entails utilizing a proxy server to retrieve content from a different URL and showcase it on the original URL. Upon a user’s access to the original URL, the request is transmitted to the proxy server, which fetches the content from the destination URL. Subsequently, the proxy server sends back the content to the user, creating the illusion that the content is hosted on the original URL.
Does URL Masking Impact SEO?
URL masking, if implemented improperly, can have implications for search engine optimization (SEO). SEO is influenced by how search engines crawl, index, and rank web pages, and changes to URL structures can impact these processes. Here are some considerations regarding URL masking and SEO:

- Indexing and Crawling Challenges: Some masking techniques, especially those involving frames or iframes, can present challenges for search engine crawlers. Search engines may have difficulty properly indexing and understanding the content within frames, leading to potential SEO issues.
- Duplicate Content Concerns: If multiple URLs display the same content due to URL masking, search engines might perceive it as duplicate content. Search engines generally aim to provide diverse and relevant results, and duplicate content can affect a website’s ranking.
- Link Equity Distribution: It can influence how link equity (also known as link juice) is distributed. If the original URL is masked and the content is fetched from another source, the link equity might not be transferred effectively, impacting the ranking of the original content.
- User Experience Matters: Search engines consider user experience as a ranking factor. If URL masking is used in a way that confuses or misleads users, it may result in a poor user experience. Search engines may penalize websites that employ deceptive practices.
- Transparency and Trust: Search engines favor transparency and authenticity. If URL masking is used for deceptive purposes or to manipulate search rankings, it can undermine the trustworthiness of the website in the eyes of search engines.
To mitigate potential negative impacts on SEO when using URL masking, consider the following best practices:
- Use SEO-friendly techniques: Implement the methods that are more search engine-friendly, such as server-side redirection, rather than approaches like frames or iframes.
- Canonicalization: Implement canonical tags to inform search engines about the preferred version of a URL when dealing with duplicate content.
- Proper Redirects: If it involves redirects, use HTTP status codes like 301 (permanent redirect) to indicate to search engines that the content has permanently moved.
- Clear Navigation: Ensure that the navigation structure of the website is clear and accessible to both users and search engine crawlers.
- Transparent Implementation: Use ethically and transparently. Provide clear and accurate information about the content being presented.
Reasons for URL Masking
URL masking, also known as URL cloaking or link masking, is employed for various reasons in different contexts. Here are some common reasons for implementing URL masking:
- Branding: URL masking allows organizations to present a consistent and branded image by using a custom domain in the address bar. This helps reinforce brand identity and recognition.
- Affiliate Marketing: Affiliates often use URL masking to hide lengthy and complex affiliate links. This not only makes the URL more aesthetically pleasing but also instills trust in users who may be skeptical of clicking on obvious affiliate links.
- User-Friendly URLs: Masking URLs can create cleaner and more user-friendly links, making them easier to remember, share, and type. This is particularly common in URL shortening services.
- Preventing Broken Links: URL masking can be used to redirect users to a new page or location without changing the displayed URL. This helps prevent broken links when content is moved or updated.
- Enhancing Security: By masking URLs, sensitive information about the underlying structure or parameters of a website may be hidden. This can add a layer of security by making it more challenging for potential attackers to discern details about the web application.
- Improved User Experience: URL masking provides a seamless user experience by maintaining the appearance of a particular domain throughout a browsing session. This can be especially relevant in situations where content is sourced from different domains.
Advantages of URL masking
- It allows for the use of custom or branded domains, contributing to a more cohesive and recognizable brand identity.
- It enables the redirection of URLs without altering the displayed URL, helping to avoid broken links during content updates or migrations.
- It facilitates the integration of content from external domains into a website, creating a unified user experience.
- Customized and masked URLs are effective for creating memorable and shareable links in marketing campaigns.
- Organizations can manage redirects effectively using URL masking, changing the destination URL without impacting the displayed URL.
Conclusion
In conclusion, URL masking serves as a valuable technique with several advantages in diverse web contexts. From enhancing branding and creating user-friendly URLs to optimizing affiliate marketing links and improving security. However, it is crucial to approach its implementation ethically, ensuring transparency and compliance with SEO best practices. By leveraging URL masking judiciously, businesses can foster a more seamless user experience, bolster brand identity, and navigate various online scenarios with greater flexibility and control.